The move towards IPv6 is not only a change in technology from IPv4 to IPv6, but also a change in internet policy, government and control of networks. With the depletion of IPv4 addresses, businesses should consider new policies, compliance standards, and operational changes occurring with the use of IPv6. Learning these policy differences between IPv4 and IPv6 will enable the organizations to sustain security, scalability, and regulative alignment in a fast-changing digital environment.
Understanding Policy Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
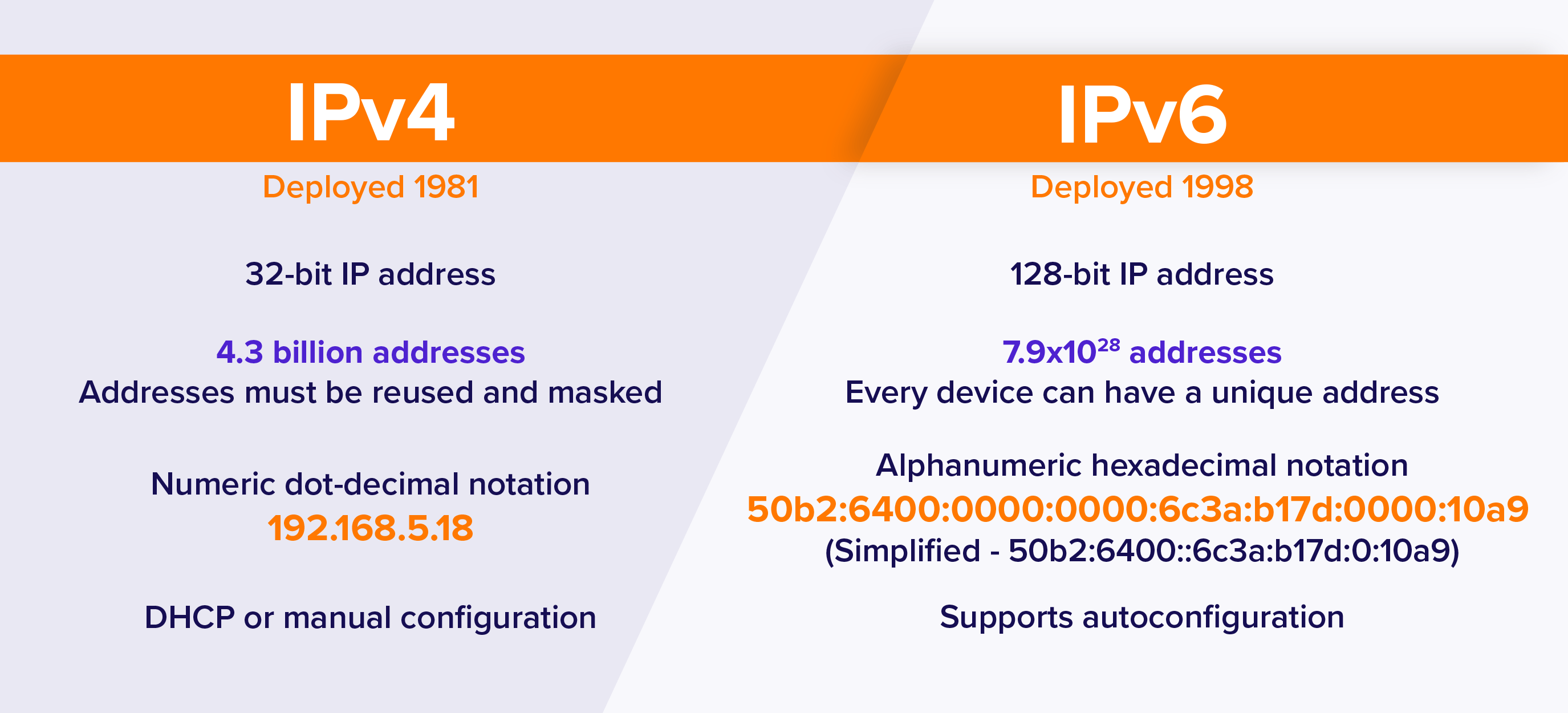
1. Address Allocation and Structure
The address size of IPv4 is 32 bits, which is no longer abundant. In IPv6, this is replace upon by the 128-bit system that has an enormous number of unique addresses. The change enables easier management of the network and enables the increasing number of connected digital devices across the globe.
2. Network Configuration and Management
IPv4 will manually configure or assign the addresses with DHCP. IPv6 makes this easier by allowing stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC) to enable automatic configuration. This simplifies the process of establishing new devices and minimizes the administrative effort. Hence, it also increases efficiency among those businesses that maintain large-scale networks.
3. Security and Data Protection Policies
The default implementation of IPv4 did not contain strong security measures, and external protocols. IPv6 has IPsec and secure communication takes place between the devices. This built-in security is in line with the current cybersecurity measures. Hence, this provides more secure data transmission through both the private and the public networks.
4. Performance and Network Efficiency
IPv6 enhances the performance, as there is no requirement for Network Address Translation (NAT). The devices are available with the labelling in unique address, reducing the complexity of routing and enhancing speed. IPv6 is also more responsive and reliable in general because the streamlined packet structure enables a faster processing speed.
5. Policy Adaptation and Global Compatibility
The network policies of governments and organizations should facilitate the use of IPv6. This is training, upgrading the system, as well as compliance modifications. The switch to IPv6 also followed a long-term compatibility with the global networks. It allows space to be innovative, increase connectivity, and get businesses ready to grow and advance digitally and technologically in the future.
Insights About Security and Policy Compliance Differences
When you buy IPv4 address, know that security policies are based on external settings such as Network Address Translation (NAT) and manual IP management, which may make them difficult to comply with. The implementation of security requires firewalls and routing tables, and therefore IPv4 networks are prone to human error.
IPv6 policies are designed with an in-built IPsec support and offer end-to-end encryption and authentication. Hence, IPv6 regulatory frameworks put privacy by design and stateless address auto-configuration (SLAAC) as a priority.
Enterprises and governments that switch to IPv6 need to revise their policy of compliance with the parameters of more rigorous encryption and authentication. IPv6 enables less trouble in compliance with regulatory measures in data protection standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and local cybersecurity regulations, to have network integrity in the future.
Facts Behind Network Management and Policy Automation
When you lease IPv4 addresses understand that the policies are mostly manual, and address assignments, subnetting, and reconfiguration must be administered by an administration. This adds to the cost of operation and mismanagement.
IPv6 presents the policy automation aspect in the form of auto-configuration, DHCPv6 and multicast addressing. Hence, this at reducing human interventions and enhancing network scale.
IPv6 policy automation also affects compliance management, as organizations may enforce policy through automated enforcement. It is centralized and optimized through AI. This is necessary to ensure that the enterprise networks are operating within the prescription of the security, privacy and performance standards, as well as minimizing administrative overhead.
The switch to IPv6 is not only a matter of additional addresses but also policy optimization and modernization in operation.
Transition and Coexistence Policies to Know
The process of switching between IPv4 and IPv6 is dual dual-stack policy. Hence, both protocols are used at the same time. RIRs and ISPs give instructions towards compatibility in the process of migrating.
The policies to rent IPv4 address decommissioning depend on the region. Government incentives are offered to adopt IPv6 or to transition the requirements of the public infrastructure.
Companies need to develop hybrid compliance models. They should retain IPv4 but implement IPv6-compatible networks. Synchronization of policies guarantees continuous connectivity, routing efficiency and compliance with regulations.
Finally, the coexistence policies influence the process of integrating the legacy and modern systems in enterprises in a secure, efficient and legal way.
FAQs: Common Questions People Often Ask
1. What is the reason why IPv4 policies are stricter than IPv6?
The policies of IPv4 are more stringent due to the lack of addresses, in which the strict ownership verification is in place. The recording is controlled by the regulation that avoids misuse or fraud.
2. Does IPv6 do away with IP trading?
Yes, largely. IPv6 has a lot of addresses and has minimized scarcity. Nevertheless, IPv4 trading is supported by the pervasive dependency of the legacy systems.
3. Is IPv4 and IPv6 under the same organizations?
Yes, they are both operated by Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) such as ARIN, RIPE and APNIC under different allocation systems.
4. What are the key policy benefits of IPv6?
IPv6 has automatic control, an inbuilt IPsec security, privacy assurance, and ease of allocation without limitations due to scarcity.
Unlock the Future of IP Trading with IPV4 TradeHub!
Ready to maximize your network assets? IPV4 TradeHub is your trusted partner for secure, compliant, and verified IPv4 transactions. Whether you are buying, selling, or leasing IP blocks, our expert team ensures smooth transfers, registry compliance, and top-market value. With industry-leading brokerage services and transparent policies, our platform helps you stay competitive in a rapidly changing internet landscape.