Modern networking is based on the Internet Protocol (IP). It allows communication between devices on the other side of the world. The most common IP standard is IPv4 or Internet Protocol Version 4, which gives each connection a unique address. Although IPv6 has become a reality, IPv4 is still invaluable in terms of its simplicity, reliability, and popularity. In the modern world, IPv4 has been popular among enterprises and Internet Service Providers (ISPs). It acts as a foundation to enable a transparent connection in the digital world. This guide explains what is the IPv4 IP and how it works in the computer network system.
Understanding What is the IPv4 IP
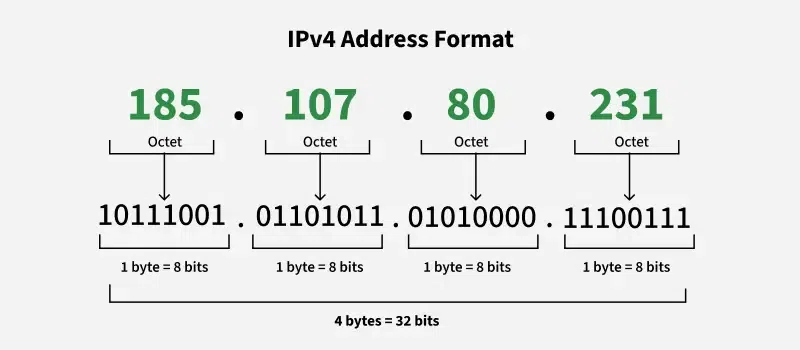
Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) is the most popular system of allocating addresses to networked devices. It enables computers, servers and other devices to discover and interact with each other on the internet or on personal networks. An IPv4 address is a 32-bit number. It comes in the form of four groups of numbers with periods between them, like 192.168.1.1.
Although IPv6 is becoming widely common, IPv4 is still necessary because it is less complex, reliable and universally accessible. Companies, Internet Service Providers and cloud providers still rely on IPv4 to access secure, efficient and reliable network connectivity.
Insights on Different Types of IPv4 Addresses
Public IPv4 Addresses
IANA and regional internet registries allocate public IPv4 addresses to devices that connect to the rest of the internet. They facilitate global interaction and the availability of internet services. The few addresses available are becoming valuable because there are few of them. Public IPv4s are the basis on which businesses and organisations have their websites, email servers and cloud services. It helps to facilitate reliability in connectivity and accessibility throughout the internet.
Private IPv4 Addresses
When buying IPv4 space know that local networks make use of the private address, which is not routable on the public internet. They are available in a range of 10.0.0.0/8 and 192.168.0.0/16. These speeches promote the internal communication among devices such as computers, printers, and routers. The use of private IPs enhances network security. Hence, it assists organizations in managing their devices effectively without necessarily using the available limited public IPv4 addresses.
Static vs Dynamic IPv4
When you lease IPv4 addresses, they are suitable for servers, hosting and enterprise systems which require stable access. DHCP is used to assign dynamic IPv4 addresses and is therefore appropriate when it comes to common gadgets such as laptops as well as mobile phones. Businesses require the reliability and hosting services of a static IP and a dynamic IP. It minimizes the management effort, as well as maximizing the utilization of addresses in large networks.
How Does it Work in Computer Systems?
In computer systems, Ipv4 for sale is used to name devices on a network, enabling them to be able to interact with one another. Every device will have a different address, be it a public address or a private address, to transmit and receive data. Routers utilize such addresses to forward information to the appropriate destination, be it within a local network or the internet.
Hence, the use of static IPs offers the benefit of providing a certain degree of permanence in identifying the servers and the critical systems. The dynamic IPs are assigned to ordinary devices, and they automatically change. This system will guarantee adequate circulation of data, avert conflicts and ensure network security. Altogether, IPv4 addressing is the foundation of digital communication that makes networks stable and systematized.
IPv4 vs IPv6: Key Differences You Should Know About
IPv4
The most popular IP addressing system is Internet Protocol version 4 or IPv4. It has a 32-bit address format, and this enables approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. The IPv4 addresses are composed of four sets of figures separated by dots, like 192. 168.0.1. It is straightforward, consistent and conforms with most networks. Nevertheless, the few addresses cannot sustain the increasing demand for devices linked to the internet, which has catalyzed the use of IPv6.
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the next-generation addressing system that is supposed to replace IPv4. It is a 128-bit format, which has an infinite number of possible addresses. Addresses of IPv6 are represented as eight blocks of hexadecimal numbers delimited by colons, such as 2001:0db8:85a3:0370:8a2e: 0370:7334. It has inbuilt enhancements of superior security, efficiency and routing as well. Through IPv6, the internet will be able to keep growing and accommodating billions of new devices and new advancements.
FAQs: Common Questions People Often Ask
1. What does IPv4 stand for?
IPv4 is the abbreviation of Internet Protocol version 4, the fourth edition of IP that is applied in addressing devices on networks.
2. Why is IPv4 still used today?
The legacy infrastructure, compatibility needs, and slower implementation of IPv6 globally have seen IPv4 still being widely used.
3. How many IPv4 addresses exist?
IPv4 can support up to 4.3 billion unique addresses, with a significant number of addresses already being used or reserved.
4. Can IPv4 and IPv6 work together?
Yes, the dual-stack configurations permit IPv4 and IPv6 to coexist in the same network.
5. Is IPv4 more secure than IPv6?
It is not IPv4 that is more secure, but rather security lies in network setups, firewalls, and monitoring procedures.
Unlock the True Value of IP Addresses with IPv4 TradeHub
IPv4 addresses are no longer just technical resources; they are high-value digital assets. At IPV4 TradeHub, we help businesses buy, sell, and lease IPv4 addresses securely and transparently. Whether you are expanding your infrastructure or monetizing unused IP space, our expert-driven marketplace ensures compliance, efficiency, and maximum ROI. Join organizations worldwide that trust us for reliable solutions and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive internet landscape.